- In RAID 1 (mirroring) data is being uninterruptedly copied from one disk to another or from one group of disks to another.
RAID 1 – “Mirror”. Minimum number of disk drives to build RAID = 2. (data is recorded to all devices in a synchronized manner and information on them is identical. Should one disk fail, information will remain because it is available on other disks as well). 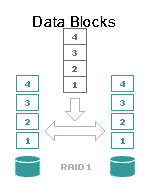
RAID 10 has combined the advantages of RAID 1 (high-performance) and RAID 0 (increased reliability). Requires minimum four hard disk drives.
RAID 0+1 (RAID 10) – Minimum number of disk drives to build RAID = 4. To build it you need to build two RAID 1 arrays and then stripe them, i.e. two RAID 1 are put in RAID 0.
JBOD is used when you need to unite several physical disks into one volume. Capacity and number of disks doesn’t matter.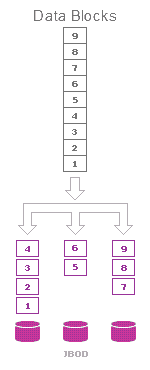
- RAID 5 – Striping + data containing checksum. Minimum number of disks to build RAID = 3.
RAID 5 mathematically calculates a value “parity” from every two disks, but does it more effectively. In case one of the disks fails the checksum will be used to recover lost data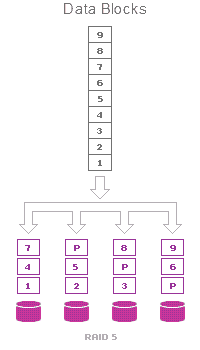 Р – checksum
Р – checksum
Hot Swap allows replacing the device on the go, in the context of our article it's a hard drive or controller (controllers with hot swap is a rarity at the same time it is a standard thing for hard drives)
- RAID 3
RAID 3 has all the advantages of RAID 10 but provides more reliable data protection owing to a mathematical expression that processes data from two storage devices and calculating a checksum (‘parity’) for writing to the third disk. Requires minimum three hard disk drives.
Myths and most common misconceptions:
Mirroring won’t give you 100% data protection guarantee
- in the event of power supply failure all your hard drives will go belly up (burn down)
- if you erased or overwrote something, you did it on all hard drives in array
- in case if controller malfunctions, data will be damaged on all hard drives in array
Stripe is not the fastest array.
- hard drives can be of different models or even worse – different manufacturers
- hard drives may not be geared to work in stripe (controller’s cache memory is not optimized, bad internal micro program and so forth)
- IDE hard drives are not geared to work with bulk queries and large dataflows.
RAID 5 is the most reliable among the most affordable systems, but it has its own disadvantages.
- disks are not eternal and sooner or later they fail and since in arrays they are from the same batch (produced at the same time) it often happens that 4 or 5 drives fail simultaneously.
- many controllers have self-healing functions and other useful disk change procedures without need to stop the array. Main problem is that controller manufacturers believe that these functions will be used by professionals, user often destroy their own data and do not even understand what they are doing.



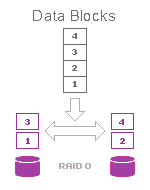
 RAID 0 (striping) unites all media in array into a single large disk.
RAID 0 (striping) unites all media in array into a single large disk.