- Home
- About Us
- Recovery Services Individual RecoveryEnterprise RecoveryAdditional Recovery
- Software
- Testimonials
- Locations
Forensic data recovery
How is forensic data recovery different to other data recovery processes and what service does the user actually require?
What is forensic data recovery…
Forensic data recovery differs quite significantly from other data recovery process, but to the user these differences may not be obvious. Whilst the end result might be the same, the way this is achieved is very different. It is important that the objectives are clear from the outset, because if the hard drives to be examined are not dealt with properly any subsequent claim may well be compromised! Quite simply the ‘forensic’ element of data recovery refers to the information being admissible for legal purposes.
Forensic data recovery is normally associated with data that will be used in legal or court proceedings, whether criminal or civil in nature. More often than not, we are engaged by solicitors where digital evidence is crucial to the outcome of the claim. Data Recovery Specialists are not legal advisers and cannot offer advice on technical areas of law. However, we are able to isolate, acquire and report on digital media and electronic evidence.
SSD vs. HDD – The Missing Considerations
Recently, there has been a lot written about Solid State Drives (SSDs) and their role in enterprise storage. These articles include several comparisons of solid state drives and mechanical drives in RAID arrays for enterprise applications. While most of these articles address several very key areas of comparison (cost, performance, capacity, power, cooling, reliability), they often neglect to consider data recovery and data destruction/asset disposal. In the first part of this three-part series, I will examine data loss and recovery. In the second part, I will examine asset disposal, and in the third article, I will discuss steps that can be taken to minimize the risks.
Let’s tackle data recovery first. To understand how your choice of storage can affect the recoverability of data in the event something happens to your storage (and your backups), we need to take a closer look at how the data from a RAID array is written to the media.
With solid state disks, the data passes through the RAID controller to the individual SSDs that make up the array. As the data reaches the individual drives, it is passed to another specialized controller called a wear-leveling controller. The wear-leveling controller then determines to which NAND chip and block inside that chip the data is electronically written. The location of the data on the NAND chips changes constantly to help protect the NAND chips from wearing out.
With mechanical disks, the data is passed from the RAID controller to the individual disks. The data is then magnetically written by the read/write head to the platters in the drives as bits. It is important to note that the data is written in a very specific pattern on the platters. Specific bits of data are stored in consistent locations. As an example, when block 10 is written to the platter, barring any defects, the block stays in the same location on the disk platters. The data can then be read from the platter by going back to the same location on the platter and reading the magnetic orientation of the bit stored there. When changes are made to the data, the orientation of the bit may change, but its location on the platter does not change.
How Server Virtualization Works
Introduction to How Server Virtualization Works
Server computers -- machines that host files and applications on computer networks -- have to be powerful. Some have central processing units (CPUs) with multiple processors that give these servers the ability to run complex tasks with ease. Computer network administrators usually dedicate each server to a specific application or task. Many of these tasks don't play well with others -- each needs its own dedicated machine. One application per server also makes it easier to track down problems as they arise. It's a simple way to streamline a computer network from a technical standpoint.
There are a couple of problems with this approach, though. One is that it doesn't take advantage of modern server computers' processing power. Most servers use only a small fraction of their overall processing capabilities. Another problem is that as a computer network gets larger and more complex, the servers begin to take up a lot of physical space. A data center might become overcrowded with racks of servers consuming a lot of power and generating heat.
Server virtualization attempts to address both of these issues in one fell swoop. By using specially designed software, an administrator can convert one physical server into multiple virtual machines. Each virtual server acts like a unique physical device, capable of running its own operating system (OS). In theory, you could create enough virtual servers to to use all of a machine's processing power, though in practice that's not always the best idea.
Virtualization isn't a new concept. Computer scientists have been creating virtual machines on supercomputers for decades. But it's only been a few years since virtualization has become feasible for servers. In the world of information technology (IT), server virtualization is a hot topic. It's still a young technology and several companies offer different approaches.
How to fix damaged restore points in VDR
VDR – VMware Data Recovery, fixing damaged restore poins.
VDR is a part of vSphere Essentials PLUS and above versions (except standard) and it’s a virtual appliance which helps you to protect your Virtual Machines running under VMware vSphere 4.x by using deduplication and CBT. It’s a simple backup solution with no e-mail reporting (yet), but which does it’s job and protecting your VMs. The solution can protect up to 100 VMs, cannot backup FT enabled VMs, RDM in physical mode not supportedVMs. And you can backup 8 VM at the same time. (per appliance).
You might run into situation,where you’ll need to fix damaged restore points. You backup stopped executing since some time, and you’re having an errors like in the screenshot below, and when digging a bit more you’ll find a restore points marked in red color (as damaged)
In fact, to see the restore points marked as red you must go to the Restore TAB and expand all restore points to see the bad ones.
You must fix that otherwise the backups won’t works. I have been experiencing this issue recently in one of our backup site. You’re having Integrity check errors with the destinations datastores locked.
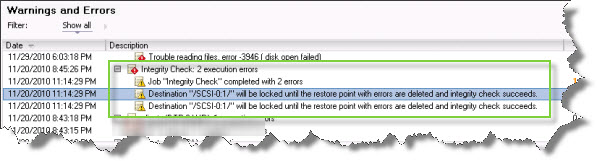
So how to fix this issue?
How To Repair A Suspect Database In MS SQL
Issue
You have a database in MS SQL that is tagged as (suspect) and you are unable to connect to the database.Possible Causes
- The database could have become corrupted.
- There is not enough space available for the SQL Server to recover the database during startup.
- The database cannot be opened due to inaccessible files or insufficient memory or disk space.
- The database files are being held by operating system, third party backup software etc.
- There was an unexpected SQL Server Shutdown, power failure or a hardware failure.
These steps require you to have Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio installed on your computer. If you do not have this installed please follow the steps outlined in the following article: How To Connect To Your MS SQL Database
Always back up the website before making any changes to the database . Shared hosting customers can do this through the Control Panel. Refer to Back Up Your Website Using Plesk. Dedicated server customers can back up the site either through the Control Panel, or through the Control Suite. Refer to How to Back Up a Domain Using Control Suite.
Copyright © 2026 DataRecoup Recovery Services. All Rights Reserved. Designed by DataRecoup Lab.