- Home
- About Us
- Recovery Services Individual RecoveryEnterprise RecoveryAdditional Recovery
- Software
- Testimonials
- Locations
Can I use S.M.A.R.T. on SSDs?
Many S.M.A.R.T. utilities were designed for hard disk drives so be sure you select a utility that is compatible with SSDs!
Can I use S.M.A.R.T. on SSDs...
S.M.A.R.T. which stands for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology is a fantastic tool for anticipating hardware errors on hard disk drives. The utility can test for bad sectors and some software can even test for temperature, core speed and system fan speed anomalies. When S.M.A.R.T. software indicates an imminent hard drive failure, the user is notified so that data can be backed up and data loss avoided. These hard drive diagnostic programs are widely used on mechanical hard disk drives and RAID, but how reliable are they on solid state drives SSDs?
Checks include electrical and mechanical performance and read/write error rates. Electrical tests include RAM and read/write circuitry. Mechanical tests seek servo information on data tracks, scanning for bad sectors across the entire disk surface. However solid state drives are constructed very differently, although flash media does develop errors over time – normally bad flash blocks in the NAND memory chips. Just like traditional hard disk drives, the controller manages these bad blocks and re-maps them to ‘extra’ blocks. Eventually the drive will run out of ‘extra’ blocks and S.M.A.R.T. is quick to identify this.
14 Ways To Get The Most From Your RAID System
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. It’s a set of independent hard drives able to provide redundancy, designed to keep the system online, and are mainly used in businesses server environments.
With the continued fall in hard drive prices, it is also becoming more common to find RAID configurations at home. Though these systems are not comparable with enterprise-class RAID systems, they are often used in cheap Network Area Storage (NAS) systems and are connected to form a home network for storing and sharing videos, photos, music and other entertainment content between multiple devices.
On the other hand, enterprise RAID storage architectures perform tasks that are usually business-critical and their efficiency and uptime are paramount. These RAID systems support the operation of virtual environments (eg. VMware & Microsoft Hyper-V), database (eg. Microsoft SQL and Oracle), email systems like Microsoft Exchange Server and all the applications that need performance, reliability and scalability.
In these situations, the failure of a RAID system paired with a data loss is a real disaster to be avoided.
To trust is good, not to trust is better
RAID systems are more reliable than the individual spinning hard drives or individual SSDs. This is true because using multiple disks and providing redundancy they can tolerate the failure of one drive in the array whilst staying online. In the event where there is a RAID system failure, the reconstruction of the information can be done using the parity calculated and stored during normal write operations.
Since to trust is good but sometimes not to trust is better, below follows a collection of comments and suggestions from our experts to help you to work better and be more comfortable with your RAID system.
27% of businesses have lost sensitive data in the last 12 months
Accidental data leaks by staff and software vulnerabilities two of the main causes of data loss, according to new study
Over a quarter of small, medium, and large businesses have lost sensitive data in the past year due to internal IT threats and a lack of cyber security, a new study by security specialist Kaspersky Lab reports.
Surveying IT professionals across the globe from 2011 to 2014, the study found that the most common cause of data loss was down to accidental leaks by staff when sharing data with 22% of all businesses having lost data due to negligent data sharing.
Software vulnerabilities was also a widely reported IT threat with 20% of businesses having lost sensitive data due to a lack of digital security on their software systems.
Other internal threats reported to have led to data loss incidents included misplaced mobile devices, intentional data leaks from employees, and security failures by a third-party supplier.
Businesses within the utilities and energy industry were the most likely to have suffered data losses with 40% of firms within the sector having encountered software vulnerabilities. The telecom sector also reported a high rate of software vulnerabilities at 35%.
Reference: http://startups.co.uk/27-of-businesses-have-lost-sensitive-data-in-the-last-12-months/
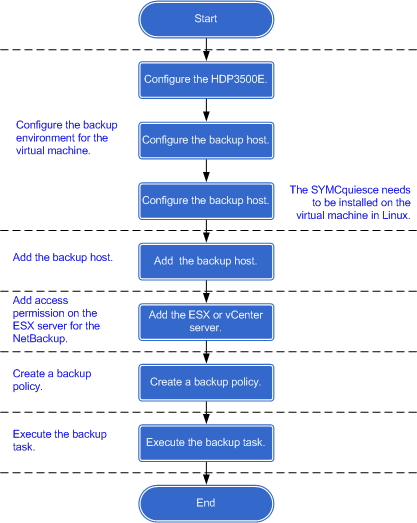
Backup of a VMware Virtual Machine (in Linux)
When file loss or system damage occurs after a Linux-based VMware virtual machine is backed up, you can recover the file or full virtual machine using backup images.
1 Configuration Process
To back up a VMware virtual machine, learn about the configuration process in advance.
2 Configuring the HDP3500E
The NetBackup uses host names to communicate with other devices on the backup domain. Therefore, add mappings between host names and IP addresses of the ESX server (or the vCenter server), virtual machine, and backup hosts before backing up the VMware virtual machine.
3 Configuring a Backup Host
A backup host performs backup tasks on behalf of VMware virtual machines. Install a NetBackup client and add mappings between host names and IP addresses of the HDP3500E and ESX server (or the vCenter server).
4 Configuring a Virtual Machine
On a virtual machine in Linux, install a NetBackup client so that a single file can be recovered. Install the SYMCquiesce to guarantee a consistent file system.
5 Adding a Backup Host
To back up a virtual machine using a backup host, add the backup host to NetBackup configuration.
6 Adding an ESX Server (or a vCenter Server)
To back up or restore a virtual machine, the NetBackup server requires login credentials of an ESX server (or a vCenter Server) to verify permission.
7 Creating a Backup Policy
A backup policy specifies backup information, including backup objects, execution time, execution frequency, storage location, and retention period.
8 Executing a Backup Task
Backups can be performed automatically based on a backup schedule or manually based on a backup policy. After a policy is created, you are advised to manually run the policy to check whether the policy functions properly.
Configuration Process
To back up a VMware virtual machine, learn about the configuration process in advance.
Figure 1 shows the configuration process for a Linux-based VMware virtual machine.
Using sp_change_users_login to fix SQL Server orphaned users
I’m going to be looking at sp_change_users_login as a continuation to a previous post where I looked at a couple of ways to transfer logins from one SQL Server to another and touched upon the issue of the orphaned “security identifier” (SID).
A typical scenario that arises is when the DBA quickly realises that the logins on the SQL Server cannot access the database. They try and add the login to the database as a user and are presented with the error:
Error 15023: User already exists in current database.
sp_change_users_login to the rescue!
I first saw this error a number of years ago and due to my complete lack of experience at the time, one of my first thoughts was that I would have to remove the database users, re-add them all for each login requiring access and then proceed to add the permissions back in for user.
Copyright © 2024 DataRecoup Recovery Services. All Rights Reserved. Designed by DataRecoup Lab.