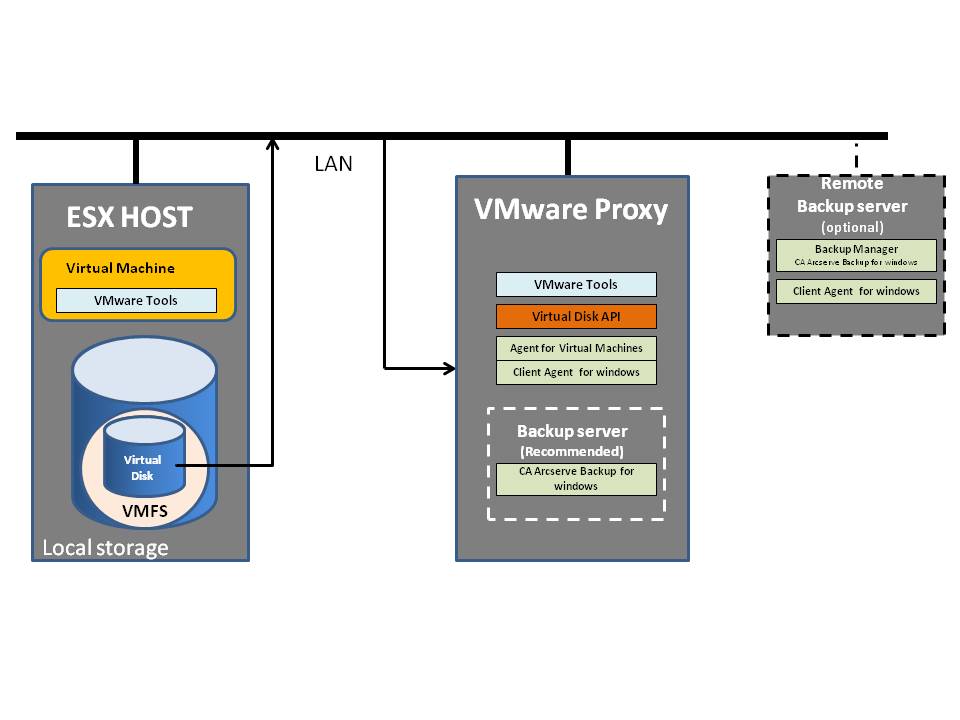
In this mode, the ESX/ESXi host reads data from storage and sends it across a network to the VMware backup proxy server. For LAN transport, virtual disks cannot be larger than 1TB each. As its name implies, this transport mode is not LAN-free, unlike SAN and HotAdd transport. LAN transport offers the following advantages:
- The ESX/ESXi host can use any storage device, including local storage or NAS.
- The VMware Backup Proxy could be a virtual machine, so you can use a resource pool and scheduling capabilities of VMware vSphere to minimize the performance impact of backup. For example, you can put the VMware Backup Proxy server in a different resource pool than the production ESX/ESXi hosts, with lower priority for backup.
- If the ESX/ESXi host and VMware Backup Proxy server are on a private network, you can use unencrypted data transfer, which is faster and consumes fewer resources than NBDSSL. If you need to protect sensitive information, you have the option of transferring virtual machine data in an encrypted form.
NFC Session Limits
NBD employs the VMware network file copy (NFC) protocol.
NFC Session Connection Limits shows limits on the number of network connections for various host types. VixDiskLib_Open() uses one connection for every virtual disk that it accesses on an ESX/ESXi host. VixDiskLib_Clone() also requires a connection. It is not possible to share a connection across disks. These are host limits, not per process limits, and do not apply to SAN or HotAdd.
| Host Platform | When Connecting | Limits You To About |
| vSphere 4 | to an ESX host | 9 connections directly, 27 connections through vCenter Server |
| vSphere 4 | to an ESX host | 11 connections directly, 23 connections through vCenter Server |
| vSphere 5 | to an ESX host | Limited by a transfer buffer for all NFC connections, enforced by the host; the sum of all NFC connection buffers to an ESXi host cannot exceed 32MB. |
| 52 connections through vCenter Server, including the above per-host limit. |
SAN Transport Mode
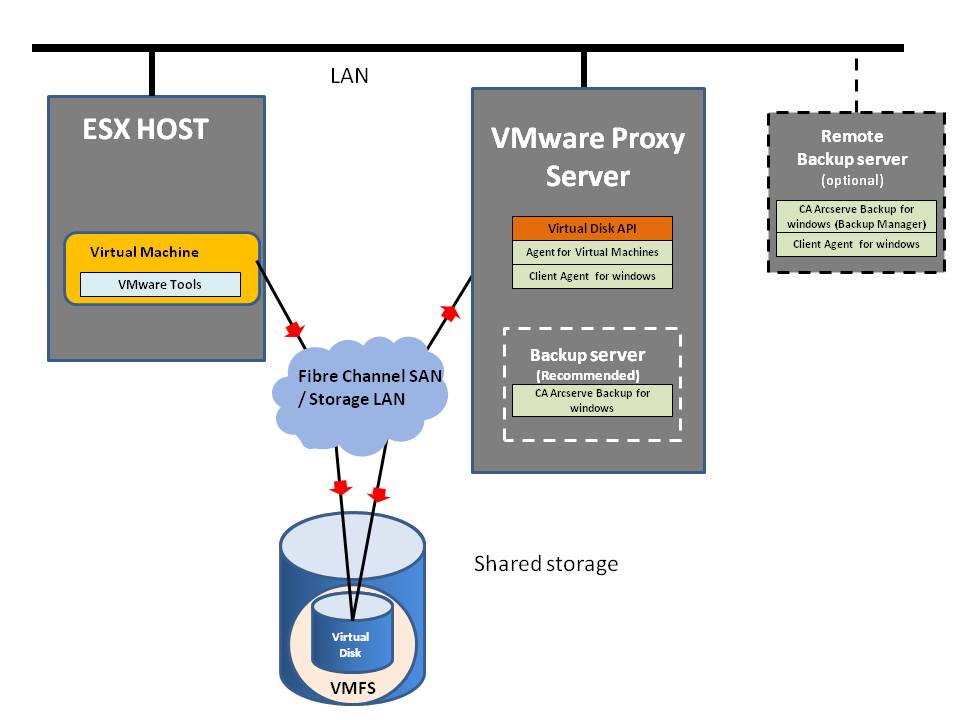
In this mode, the virtual disk library obtains information from an ESX/ESXi host about the layout of VMFS LUNs, and using this information, reads data directly from the SAN or iSCSI LUN where a virtual disk resides. This is the fastest transport method for applications deployed on a SAN-connected ESX/ESXi host.
SAN mode requires applications to run on a physical machine (VMware proxy server to be configured as a backup server, for example) with access to FibreChannel or iSCSI SAN containing the virtual disks to be accessed. This is an efficient data path, as shown in
SAN Transport Mode for Virtual Disk, because no data needs to be transferred through the production ESX/ESXi host. If the VMware Backup Proxy is also a Backup server, with optical media or tape drives, backups can be made entirely LAN-free.
ISCSI : ISCSI targets where virtual disks reside should be visible in windows disk management.
SAN : The SAN LUNS where virtual disks reside should be marked to the backup server and should be detected in windows disk management.
Best practices when using advanced transport for backup and restore (1035096)
SAN Transport Mode for Virtual Disk
HotAdd Transport Mode
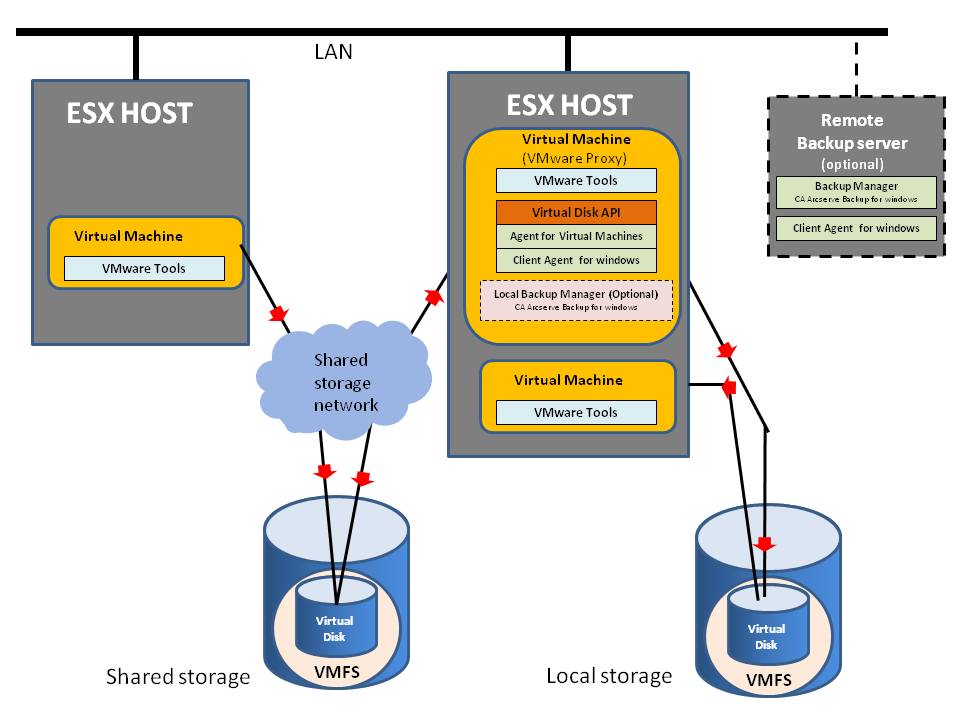
If the application runs in a virtual machine, it can create a linked-clone virtual machine from the backup snapshot and read the linked clone’s virtual disks for backup. This involves a SCSI HotAdd on the host where the application is running – disks associated with the linked clone are HotAdded on the virtual machine. VixTransport handles the temporary linked clone and hot attachment of virtual disks. VixDiskLib opens and reads the HotAdded disks as a “whole disk” VMDK (virtual disk on the local host). This strategy works only with virtual machines with SCSI disks and is not supported for backing up virtual machines with IDE disks.
HotAdd Transport Mode for Virtual Disk
SCSI HotAdd is a good way to get virtual disk data from guest virtual machines directly to the ESX/ESXi host on which they are running.
Running the VMware Backup Proxy server on a virtual machine has two advantages: it is easy to move a virtual machine to a new media server, and it can also back up local storage without using the LAN, although this incurs more overhead on the physical ESX/ESXi host than when using SAN transport mode.
Limitation with Mismatched Block Size
HotAdd cannot be used if the VMFS block size of the datastore containing the virtual machine folder for the target virtual machine does not match the VMFS block size of the datastore containing the proxy virtual machine. For example, if you back up virtual disk on a datastore with 1MB blocks, the proxy must also be on a datastore with 1MB blocks.
Licensing.
n vSphere 5.0, the SCSI HotAdd feature is enabled only for vSphere editions Enterprise and higher, which have Hot Add licensing enabled. No separate Hot Add license is available for purchase as an add-on. In vSphere 4.1, Hot Add capability was also allowed in Advanced edition. Therefore, customers with vSphere Essentials or Standard edition who use backup products (including VMware Data Recovery) are not able to perform proxy-based backup, which relies on SCSI HotAdd. Those customers must use alternate transport modes. In cases where hotadd is not supported it may switch to LAN (NBD) transport mode for Virtual Disk.
Reference: http://arcserve-knowledgebase.com/index.php?View=entry&EntryID=2659